SOLAR AND DESIGN CONTROL
With its unique characteristics of resistance, durability and versatility, the glass is one of the materials used in construction which still has much more to offer and it isn’t a out of stock product in an available way.
Glass helps developing unique projects, whether in large-scale emblematic buildings or in the modern residential sector where more and more glass facades have a significant importance.
Solar Orientation
Glass areas positioning towards the sun are decisive when it comes to define the need to control heat input, solar profits.
Energy profits, or heat input, is measured by the total amount of incident solar energy as having a correct notion of solar input on glasses will easily allow to determine solar control needs, for example, in Portugal, if the glass area is faced north, the need for a solar control is almost irrelevant, as there is no sunlight, but if it is in the south/west, energy profits, heat input, this need will be very high and carefully defined.
Energy Profits Or Heat Input
Incident solar radiation on glass areas is responsible for light and heat entrance.
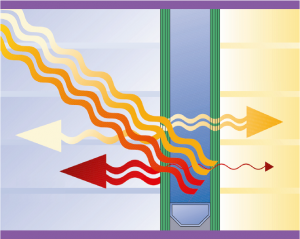 From the total amount of incident solar energy there is a percentage reflected by the glass, another percentage passes directly through the glass and another percentage is absorbed by it, from this absorbed percentage, a percentage disappears to the outside and another one disappears in it. The percentage which passes through the glass, together with the percentage which disappears in it, make up the total amount of energy which passes through the glass. This total of total energy which passes through the glass is called the Solar Factor (SF) or g-value.
From the total amount of incident solar energy there is a percentage reflected by the glass, another percentage passes directly through the glass and another percentage is absorbed by it, from this absorbed percentage, a percentage disappears to the outside and another one disappears in it. The percentage which passes through the glass, together with the percentage which disappears in it, make up the total amount of energy which passes through the glass. This total of total energy which passes through the glass is called the Solar Factor (SF) or g-value.
The Solar Factor, measured with percentage as unit, represents the total heat which passes through the glass and the closest to the zero the less heat passes through the glass.
Glass choice with a bigger or smaller Solar Factor will help on heat control, if the main purpose is heat input, choosing a glass will depend on the higher Solar Factor, if it is to shorten heat input, then the choice will depend on the lower Solar Factor.
Solar control and the light
Choosing glass with higher or lower light transmittance is crucial to acquire comfortable and transparent spaces. We often find solutions which due to its high light transmittance there is a need to use curtains or other ways to help controlling light, transparent spaces become opaque spaces, not beneficiating any more of glass as a transparent element. On the contrary, to avoid heat input, we often find solutions which in darker spaces there is a need to use electric light, constantly turned on to beneficiate from a pleasant environment to leisure or work.
The key to overcome this difficulty remains in the selection of glass, choosing glass solutions which allow heat control and at the same time define the correct light amount so that the space is comfortable and energy-efficient.
Aesthetics and Colour
The look of the glass is usually a decisive criterion in choosing a solution. In residential buildings there is normally an option for more transparent solutions and less reflective, but in office buildings or glass walls, the choice is in more or less reflective, coloured or maximum transparency solutions.
In glass facades where all the building wall is usually in glass, glass selection has to take into account blind spots, assuring uniformity in the facade.
The choice of glasses with a high light reflecting index may help in the increasing of space privacy. On the other hand, it can be a discomfort to the surrounding buildings at certain time of the day, as they can direct sunlight reflection to areas where this level of existence wouldn’t exist.
The choice of coloured glasses in the mass the Silver, Bronze, Green, Grey, Blue SOLARLUX segment, among others, allows uniformity and elegance, developing ideal solutions to uniformed glass facades.





